
The following operations can be performedĢ*x - multiplication 3/x - division x^2 - squaring x^3 - cubing x^5 - raising to the power x + 7 - addition x - 6 - subtraction Real numbers insert as 7. in science and engineering, systems of differential equations cannot be integrated to give an analytical solution, but rather need to be solved numerically. The error function erf(x) (integral of probability), Hyperbolic cosecant csch(x), hyperbolic arcsecant asech(x), Nonhomogeneous Second-Order Differential Equations To solve ay +by +cy f (x) we first consider the solution of the form y yc +yp where yc solves the differential equaiton ay +by +cy 0 and yp solves the differential equation ay + by + cy f (x). Secant sec(x), cosecant csc(x), arcsecant asec(x),Īrccosecant acsc(x), hyperbolic secant sech(x), Other trigonometry and hyperbolic functions: That is the main idea behind solving this system using the model in Figure 1.6. The Scope is used to plot the output of the Integrator block, x(t). Hyperbolic arctangent atanh(x), hyperbolic arccotangent acoth(x) 4 solving differential equations using simulink the Gain value to '4.' Then, using the Sum component, these terms are added, or subtracted, and fed into the integrator.

Such systems occur as the general form of (systems of) differential equations for vectorvalued. Hyperbolic arcsine asinh(x), hyperbolic arccosinus acosh(x), In mathematics, a differential-algebraic system of equations (DAEs) is a system of equations that either contains differential equations and algebraic equations, or is equivalent to such a system. Hyperbolic tangent and cotangent tanh(x), ctanh(x) Hyperbolic sine sh(x), hyperbolic cosine ch(x), Sinus sin(x), cosine cos(x), tangent tan(x), cotangent ctan(x)Įxponential functions and exponents exp(x)Īrcsine asin(x), arccosine acos(x), arctangent atan(x), The modulus or absolute value: absolute(x) or |x|
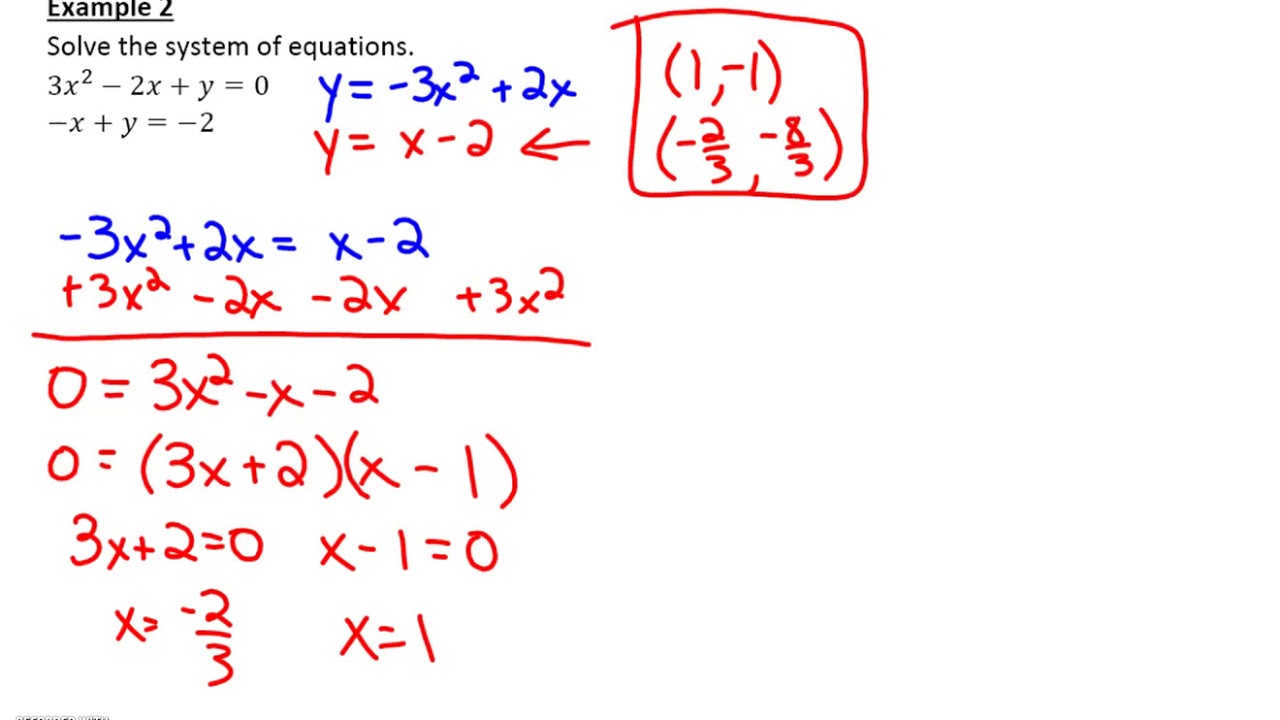
A system of two equations with two unknowns.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
